Discover the Consequences of Eating Below Your Resting Metabolic Rate!
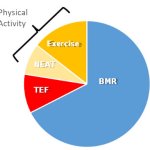
Are you eating enough to support your metabolism? Your resting metabolic rate (RMR) is the minimum number of calories your body needs to maintain basic physiological functions at rest. Eating [...]


 g, and becoming fit.
g, and becoming fit.