Unlocking the Secrets to Accurate Resting Metabolic Rate Calculations for Bulking and Cutting Success
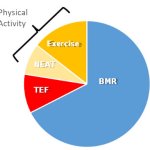
Limitations of Common Resting Metabolic Rate Equations In a recent article titled “Most metabolic rate prediction equations are bad when weight is stable, and worse when it [...]


 g, and becoming fit.
g, and becoming fit.